Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation test
synchrotron X-ray scattering and nanoindentation testIm, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Choe, H.*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Lim, S.*; et al.
Construction and Building Materials, 365, p.130034_1 - 130034_18, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:70.19(Construction & Building Technology)Ohira, Saki; Iida, Yoshihisa
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/02
The sorption distribution coefficient ( d) of niobium-94 (Nb-94) on minerals is one of the important parameters in safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. In a previous study, the
d) of niobium-94 (Nb-94) on minerals is one of the important parameters in safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. In a previous study, the  d values of Nb under alkali condition in the presence of Ca, were two orders of magnitude higher than those in the presence of Na. In this study, Nb sorption experiments were performed to reexamine the effect of Ca on Nb sorption on clay minerals, and blank tests were performed to check for precipitation formation. The results showed that the Nb sorption onto montmorillonite and illite, did not depend on the Ca concentration, and
d values of Nb under alkali condition in the presence of Ca, were two orders of magnitude higher than those in the presence of Na. In this study, Nb sorption experiments were performed to reexamine the effect of Ca on Nb sorption on clay minerals, and blank tests were performed to check for precipitation formation. The results showed that the Nb sorption onto montmorillonite and illite, did not depend on the Ca concentration, and  d values obtained in the presence of Ca were the same as those in the absence of Ca. A sorption model assuming sorption by complexation on the mineral surface was developed and then calculated using the geochemical calculation code. The model with the surface species X_ONb(OH)
d values obtained in the presence of Ca were the same as those in the absence of Ca. A sorption model assuming sorption by complexation on the mineral surface was developed and then calculated using the geochemical calculation code. The model with the surface species X_ONb(OH) and X_ONb(OH)
and X_ONb(OH)
 represented trends in the data obtained.
represented trends in the data obtained.
Kim, G.*; Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Cho, S.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; et al.
Cement and Concrete Research, 159, p.106869_1 - 106869_17, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:87.96(Construction & Building Technology)Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Irisawa, Keita; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Watanabe, Masayuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153170_1 - 153170_7, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Koyama, Taku*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Kim, J.*; Bae, S.*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 104(9), p.4803 - 4818, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:85.31(Materials Science, Ceramics)Miyajima, Yusuke*; Saito, Ayaka*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Hirata, Takafumi*
Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 45(1), p.189 - 205, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.77(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Uncertainty for elemental and isotopic analyses of calcite by LA-ICP-MS is largely controlled by the homogeneity of the reference materials (RMs) used for normalization and validation. In order to produce calcite RMs with homogeneous elemental and isotopic compositions, we incorporated elements including U, Pb, and rare earth elements into calcite through heat- and pressure-induced crystallization from amorphous calcium carbonate that was precipitated from element-doped reagent solution. X-ray absorption spectra showed that U was present as U(VI) in the synthesized calcite, probably with a different local structure from that of aqueous uranyl ions. The uptake rate of U by our calcite was higher in comparison to synthetic calcite of previous studies. Variations of element mass fractions in the calcite were better than 12% 2RSD, mostly within 7%. The  Pb/
Pb/ Pb ratio in the calcite showed
Pb ratio in the calcite showed  1% variations, while the
1% variations, while the  U/
U/ Pb ratio showed 3-24% variations depending on element mass fractions. Using the synthetic calcite as primary RMs, we could date a natural calcite RM, WC-1, with analytical uncertainty as low as
Pb ratio showed 3-24% variations depending on element mass fractions. Using the synthetic calcite as primary RMs, we could date a natural calcite RM, WC-1, with analytical uncertainty as low as  3%. The method presented can be useful to produce calcite with controlled and homogeneous element mass fractions, and is a promising alternative to natural calcite RMs for U-Pb geochronology.
3%. The method presented can be useful to produce calcite with controlled and homogeneous element mass fractions, and is a promising alternative to natural calcite RMs for U-Pb geochronology.
Onishi, Takashi; Koyama, Shinichi; Mimura, Hitoshi*
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 31(3), p.43 - 49, 2020/10
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(9), p.1062 - 1073, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)The interaction of cesium hydroxide and a calcium silicate insulation material was experimentally investigated at high temperature conditions. A thermogravimetry equipped with differential thermal analysis was used to analyze thermal events in the samples of mixed calcium silicate and cesium hydroxide under Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 with maximum temperature of 1100
0 with maximum temperature of 1100 C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca
C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca Si
Si 0
0 (0H)
(0H) ), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730
), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730 C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0
C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0 ), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100
), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100 C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H
C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0
0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0 was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
Irisawa, Keita; Garcia-Lodeiro, I.*; Kinoshita, Hajime*
Cement and Concrete Research, 128, p.105951_1 - 105951_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.84(Construction & Building Technology)This study investigated characteristics of a calcium aluminate cement modified with a phosphate (CAP) by changing an amount and concentration of mixing solution with sodium polyphosphate. When the amount of mixing solution was increased with a constant amount of sodium polyphosphate, an enhanced consumption of monocalcium aluminate was observed compared with gehlenite in calcium aluminate cement (CAC). Formation of gibbsite, Al(OH) , was also increased as a hydration product in the CAP and the possible reduction of water in the amorphous gel phase. When the amount of mixing solution was increased with a constant concentration of sodium polyphosphate, the enhanced consumption of monocalcium aluminate was not observed. Neither gibbsite nor any other crystalline hydration products were identified in this series. In addition, unreacted sodium polyphosphate remained in the system. The increased formation of gibbsite and the possible reduction of water from the amorphous gel phase appears to contribute to the improvement of the microstructure in the products.
, was also increased as a hydration product in the CAP and the possible reduction of water in the amorphous gel phase. When the amount of mixing solution was increased with a constant concentration of sodium polyphosphate, the enhanced consumption of monocalcium aluminate was not observed. Neither gibbsite nor any other crystalline hydration products were identified in this series. In addition, unreacted sodium polyphosphate remained in the system. The increased formation of gibbsite and the possible reduction of water from the amorphous gel phase appears to contribute to the improvement of the microstructure in the products.
Garcia-Lodeiro, I.*; Irisawa, Keita; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kinoshita, Hajime*
Proceedings of 15th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement (ICCC 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/09
The immobilization of low or intermediate-level radioactive wastes in cements is a common practise. Grout, a mixture of Portland cement and supplemental cementitious materials, is commonly used to encapsulate the wastes. However, the conventional cementing process based on portland cement has the risk of hydrogen gas generation, due to the radiolysis of the water intrinsically present in the cement matrix both in the pore solution and the hydrated products. The addition of phosphates to calcium aluminate cement (CAC) is interesting because this system sets and hardens via the acid-based reaction, between the acid phosphate solution and the basic CAC cement. Due to this different mechanism of reaction, it would be possible to generate a solid cementitious product with a reduced water content, which can be beneficial to minimize the risk of hydrogen gas generation associated with the radiolysis of water by radioactive wastes. The present study investigates the effect of water reduction on a phosphate modified CAC systems at different temperatures (35 C, 60
C, 60 C, 95
C, 95 C, 110
C, 110 C,180
C,180 C) in the initial 7 days of curing. Experimental results indicate that these phosphate-based cements do not form the conventional CAC crystalline hydration products in the condition tested, but provide a structural integrity despite a significant amount of water loss. The results also suggest the formation of hydroxyapatite in samples cured at 95
C) in the initial 7 days of curing. Experimental results indicate that these phosphate-based cements do not form the conventional CAC crystalline hydration products in the condition tested, but provide a structural integrity despite a significant amount of water loss. The results also suggest the formation of hydroxyapatite in samples cured at 95 C.
C.
Garcia-Lodeiro, I.*; Lebon, R.*; Machoney, D.*; Zhang, B.*; Irisawa, Keita; Taniguchi, Takumi; Namiki, Masahiro*; Osugi, Takeshi; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kinoshita, Hajime*
Proceedings of 3rd International Symposium on Cement-based Materials for Nuclear Wastes (NUWCEM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2018/11
Garcia-Lodeiro, I.*; Irisawa, Keita; Jin, F.*; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kinoshita, Hajime*
Cement and Concrete Research, 109, p.243 - 253, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:69.09(Construction & Building Technology)Nara, Yoshitaka*; Kuwatani, Ryuta*; Kono, Masanori*; Sato, Toshinori; Kashiwaya, Koki*
Zairyo, 67(7), p.730 - 737, 2018/07
Information of confining ability of rock is important for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes. To maintain or improve the confining ability of rocks, it is important to seal pores and cracks. In this study, we investigated the precipitation of minerals on the rock surface. As rock samples, we used Berea sandstone and Toki granite in this study. It was shown that precipitation occurred on the surface of rock specimens kept in calcium hydroxide solution for 1 month if the concentration was high. Specifically, if the concentration of calcium hydroxide solution was higher than 300 mg/l, the precipitation occurred obviously. After keeping rock specimens in calcium hydroxide solution, the weight of the rock samples increased and the concentration of calcium ion decreased by the precipitation. It is considered that the calcium ion in water was used for the precipitation on rock surfaces. Since the precipitation has been recognized for rock surfaces, it is possible to seal pores and cracks in rocks. Therefore, it is also possible to keep or decrease the permeability of rocks by the precipitation of calcium compounds.
 Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrier
Cm collisions 10% above the Coulomb barrierG tz, M.*; G
tz, M.*; G tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D
tz, S.*; Kratz, J. V.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th
llmann, Ch. E.*; Mokry, Ch.*; Runke, J.*; Th rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch
rle-Pospiech, P.*; Wiehl, N.*; Sch del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
del, M.; Ballof, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 961, p.1 - 21, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:47.01(Physics, Nuclear)The kinematics of multi-nucleon transfer reactions in the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Cm collisions were investigated using a stacked-foil technique and radiochemical separations. In previous studies, isotopic distributions of the products of below-target isotopes were found to be broader than those of above-target isotopes, which had been interpreted as larger contributions of strongly dumped collisions in the productions of below-target isotopes than above-target ones. However, in the present study, the average total kinetic energy loss (TKEL), and thus, the average excitation energies were determined for both below-target and above-target isotopes, and they were found to be similar. This contradicts the previous interpretation, and thus, a new interpretation has been proposed; highly excited above-target products are lost by fission.
Irisawa, Keita; Taniguchi, Takumi; Namiki, Masahiro; Garc a-Lodeiro, I.*; Osugi, Takeshi; Sakakibara, Tetsuro; Nakazawa, Osamu; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kinoshita, Hajime*
a-Lodeiro, I.*; Osugi, Takeshi; Sakakibara, Tetsuro; Nakazawa, Osamu; Meguro, Yoshihiro; Kinoshita, Hajime*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2017/04
A solidification technique with minimized water content is being developed using phosphate cements for the safe storage of secondary radioactive wastes in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Conventional cement systems become solidified via hydration reactions, and need a certain water content. Phosphate cement systems, however, become solidified via an acid-base reaction, and so they only require water mainly for reasons of workability. A reduced water content of phosphate cement systems is beneficial for the immobilization of the radioactive wastes from mitigating the potential to generate hydrogen gas by the radiolysis of water by radioactive wastes. The current study investigated the water content and mineralogy of calcium aluminate cement (CAC) and phosphate-modified CAC (CAP) cured in open systems at 60, 90 and 120  C and in a closed system at 20
C and in a closed system at 20  C as a reference case. Water contents in both the CAC and the CAP were seen to decrease as curing progressed. For
C as a reference case. Water contents in both the CAC and the CAP were seen to decrease as curing progressed. For  90
90  C, the CAP contained less water than CAC. Free water in CAC converted to structural water by heat treatment, but this was not the case for CAP. An orthophosphate hydrate salt, a precursor phase of hydroxyapatite, was found in CAP when cured at 20 and 60
C, the CAP contained less water than CAC. Free water in CAC converted to structural water by heat treatment, but this was not the case for CAP. An orthophosphate hydrate salt, a precursor phase of hydroxyapatite, was found in CAP when cured at 20 and 60  C, and a mixture of the orthophosphate hydrate salt and hydroxyapatite, Ca
C, and a mixture of the orthophosphate hydrate salt and hydroxyapatite, Ca (PO
(PO )
) (OH)
(OH) , were formed in the CAP when cured at 90
, were formed in the CAP when cured at 90  C. Phosphate products in CAP cured at 120
C. Phosphate products in CAP cured at 120  C appears to consist of a different phosphate phase compared with the CAP cured at 20, 60 and 90
C appears to consist of a different phosphate phase compared with the CAP cured at 20, 60 and 90  C.
C.
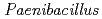 sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ions
sp. strain TCA20, isolated from a hot spring containing a high concentration of calcium ionsFujinami, Shun*; Takeda, Kiyoko*; Onodera, Takefumi*; Sato, Katsuya; Sano, Motohiko*; Takahashi, Yuka*; Narumi, Issey*; Ito, Masahiro*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(5), p.e00866-14_1 - e00866-14_2, 2014/09
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Watanabe, Kazuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(4), p.305 - 310, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)We are developing an resonance ionization spectrometric apparatus aiming at an analysis of a radioactive isotope of calcium ( Ca) in nuclear waste materials. The developed system consists of the reference laser whose frequency was locked on a Doppler-free absorption line of 85Rb and the computer-controlled fringe offset lock system which transfer frequency stability of the reference laser to slave lasers for Ca excitation. With heterodyne spectroscopy and laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca, it was confirmed that the developed apparatus was suitable for resonance ionization spectrometric analysis.
Ca) in nuclear waste materials. The developed system consists of the reference laser whose frequency was locked on a Doppler-free absorption line of 85Rb and the computer-controlled fringe offset lock system which transfer frequency stability of the reference laser to slave lasers for Ca excitation. With heterodyne spectroscopy and laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca, it was confirmed that the developed apparatus was suitable for resonance ionization spectrometric analysis.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Kato, Masaaki; Oba, Masaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Watanabe, Kazuo
JAERI-Tech 2004-065, 19 Pages, 2004/10
In nuclear waste materials there are various radionuclides to which standard analytical techniques are difficult to be applied. We are developing an analytical technique where such nuclides are ionized and mass-analyzed using diode laser based multi-step RIMS technique. The diode laser, however, has one drawback, i.e. its oscillation wavelength is readily drifted by acoustic, electric and optical noise, and thus the laser without frequency stabilization is not suitable for the analysis. In this study, we have developed (1) the diode laser whose frequency is stabilized to an intense absorption line of Rb by Zeeman effect and (2) the stabilization system where diode lasers for 3-step ionization of Ca are locked to the Rb-stabilized laser using a Fabry-perot interferometer. Additionally, to evaluate overall frequency stability of the stabilization system, fluctuations in the photoion and fluorescence signals arising from 3-step RIMS of Ca were simultaneously observed.
Hiura, Nobuo*; Yamaura, Takayuki; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*; Kobiyama, Mamoru*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 1(2), p.202 - 208, 2002/06
The purpose of this study is to develop oxygen sensor which can measure the oxygen potential of the fuel in a nuclear reactor. The oxygen sensor with CaO stabilized zirconia solid electrolyte has been specially designed in order to prolong its life time. Electromotive force (EMF) of solid galvanic cell Ni/NiO|ZrO -CaO|Fe/FeO was measured in both the out-pile tests and the in-situ tests using Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR), and the characteristics of EMF was discussed. In the out-pile test, it was found that the EMF was almost equal to the theoretical values at temperatures ranging from 700 to 1,000
-CaO|Fe/FeO was measured in both the out-pile tests and the in-situ tests using Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR), and the characteristics of EMF was discussed. In the out-pile test, it was found that the EMF was almost equal to the theoretical values at temperatures ranging from 700 to 1,000 , and the life span of the sensor was very long up to 980h at 800
, and the life span of the sensor was very long up to 980h at 800 . In the in-situ test, it was found that the EMF showed almost the reliable values up to 300 h (neutron fluence (E
. In the in-situ test, it was found that the EMF showed almost the reliable values up to 300 h (neutron fluence (E  1 MeV) 1.5
1 MeV) 1.5 10
10 m
m ), at temperatures from 700 to 900
), at temperatures from 700 to 900 . The imprecision of the EMF was found to be within 6% of the theoretical values up to 1,650 h irradiation time (neutron fluence (E
. The imprecision of the EMF was found to be within 6% of the theoretical values up to 1,650 h irradiation time (neutron fluence (E  1 MeV) 8.0
1 MeV) 8.0 10
10 m
m ) at 800
) at 800 . The oxygen sensors were found to be applicable for the oxygen potential measurement of the fuels in a reactor.
. The oxygen sensors were found to be applicable for the oxygen potential measurement of the fuels in a reactor.
Nagao, Seiya;
Marine Geology, 109, p.83 - 94, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:77.51(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English